DNA Test for Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (also known as Stein-Leventhal syndrome) is a condition in which multiple benign tumors (cysts) form in the ovaries. This happens due to increased sensitivity to male sex hormones, androgens. A high concentration of androgens causes the egg cells to remain trapped in the follicles, which later develop into cysts. As a result, ovarian functions are disrupted, ovulation becomes less frequent or may stop entirely.
The condition can be secondary (acquired), but in most cases, polycystic ovary syndrome has a hereditary nature. The first signs of the disorder often appear during puberty.
The syndrome does not depend on a woman’s ethnic background and occurs with equal likelihood in all populations. It affects about one in five women of reproductive age. However, symptoms manifest in only 5-10% of cases, which means the condition is often undiagnosed in time.
Order a mobile service visit to your home or office.
Same-day service is available.
For a free consultation, please call:
+7 (499) 490-28-01Unfortunately, in 10% of women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), symptoms may not appear until serious complications develop. The primary symptom is a disrupted menstrual cycle or its complete cessation. In addition, patients may experience:
- Periodic uterine bleeding;
- Male-pattern baldness due to excess male hormones;
- Accumulation of fat tissue in the lower abdomen and abdominal cavity, characteristic of males;
- Appearance of acne and pimples;
- Excessive hair growth in areas atypical for women;
- Increased sweating and oily skin;
- Breast reduction;
- Chronic pain in the lower abdomen.
Rapid and sudden weight gain is one of the earliest signs of polycystic ovary syndrome. In 70% of cases, obesity is diagnosed in women with this syndrome.

The studied genes

This testing panel is designed to identify genetic predisposition to polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). The DNA analysis includes the most significant and common mutations that may lead to the development of the pathology:
- Gene AR — encodes androgen receptors. Clinically important is the number of repeats of the (CAG)n sequence (cytosine-adenine-guanine), where n indicates the number of repeats. These sequences are located in the AR gene.
Marker (CAG)n, variant S, where the number of repeats is less than 18. Indicates increased sensitivity to male hormones (androgens). The presence of this mutation is associated with a higher risk of decreased cellular insulin sensitivity.
Marker (CAG)n, variant L, where the number of repeats is more than 22. Indicates reduced sensitivity to androgens. This mutation leads to increased testosterone production and raises the risk of developing polycystic ovary syndrome.
- Gene INS (VNTR repeats) — proinsulin gene, encodes the enzyme tyrosine phosphatase. The gene’s activity increases the permeability of the cell membrane for monosaccharides, fatty acids, and amino acids. Mutations in the INS gene can lead to diabetes mellitus and pancreatic cancer. VNTR polymorphism causes hyperinsulinemia, a condition that stimulates excessive androgen hormone production, which may contribute to PCOS.
- Gene PPARG — encodes a nuclear receptor that activates peroxisome proliferation. It participates in carbohydrate and fatty acid metabolism. Mutations in the PPARG gene lead to insulin resistance. This condition is accompanied by elevated insulin levels, stimulating excessive testosterone production and resulting in PCOS.
Additionally, mutations in the PPARG gene are a cause of type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Women with a family history of polycystic ovary syndrome are strongly recommended to undergo this genetic test. Heredity is the main risk factor for developing the syndrome. Genetic predisposition may also be indicated by cases of ovarian cancer in close relatives or infertility.
Other aggravating factors that contribute to the formation of multiple cysts include:
- Disorders of the pituitary gland and hypothalamus;
- Presence of diabetes mellitus;
- Adrenal gland dysfunction;
- Pancreatic pathologies;
- Acute viral infections of the reproductive system;
- Obesity;
- Exposure to cold;
- Poor environmental conditions;
- High physical stress during childhood.
All these factors negatively affect the hormonal balance of the female body. Excessive androgen production and reduced progesterone secretion can lead to complete infertility.
DNA Laboratory licenses and certificates
How to take a DNA test for predisposition to polycystic ovary syndrome?
Genetic analysis uses samples of buccal epithelium (cheek swab) or venous blood in the amount of 5–10 ml.
Venous blood
For blood collection, a vacuum tube with a purple cap is required. The tube must contain Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) of type K1, K2, or K3. The blood volume should be between 2 ml and 6 ml. Using two tubes is allowed.
The collection is performed with the patient sitting. Blood flow must go directly into the tube. After the procedure, shake the tube 5–6 times to mix the blood with EDTA.
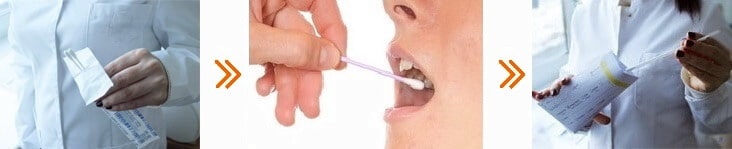
Buccal epithelium
To provide a cheek epithelial sample, you can visit specialists at a biomaterial collection point or collect the sample yourself at home. For this, you need:
- cotton swabs — at least 2 pieces, preferably 4;
- a clean paper envelope — 1 piece;
- a pair of sterile disposable gloves — 1 pair.
Or you can order a free collection kit by phone from our DNA center, which already contains everything you need. Watch the detailed instruction with video: How to take a sample.
How long does it take?

The turnaround time for the analysis is 5 business days from the moment the samples arrive at the laboratory.
The day of sample delivery is not counted, as all samples first go through a registration process before being forwarded to the genetic specialists.
How to Receive the Report
You can receive your DNA test results in any convenient way:
- Electronically via email;
- In person at the biological sample collection point;
- By delivery through Russian Post;
- By courier delivery to your door;
- By phone (if you have a unique order number, and the phone number is authorized to receive verbal results).
The method of result delivery is selected when placing the order for the analysis.
Where to get a DNA test for polycystic ovary syndrome
Take a DNA test for polycystic ovary syndrome
- You can use the form «Pre-appointment» to schedule an appointment or come to our genetic center at any time convenient for you.
See step-by-step instructions see here. - Do it yourself at home:
- Order by courier our branded kit, specially designed for self-collection of DNA samples.
- Using ordinary cotton swabs (ear swabs) from a pharmacy. Our instructions.
- Order a specialist visit to your home for free.
Why the DNA Center «DTL» is the Best in Moscow
How to pay for a DNA test for polycystic ovary syndrome
For your convenience, there are several cash and non-cash payment options for a DNA test:
- In our DNA centers, you can pay in cash or with a bank card.
- Online payment is available on our DNA center website.
- At the offices of Sberbank or any other Bank by receipt (download).
- Through a bank account (for legal entities).
When filling out an application for DNA analysis, you can choose the method of receiving the genetic test results:
- In person at the DNA center.
- To the e-mail specified in the application for analysis.
- By courier service throughout Russia.
- If you have taken a legal DNA test, we can send the forensic genetic report to the address of the court.
- If you need another delivery method, you can specify it in the application.
Each order is assigned a unique individual number. The laboratory guarantees 100% safety and confidentiality of all data received from you.
What should I do if the test is positive?
A positive test result indicates the presence of a pathological gene variant that increases the risk of developing a malignant tumor. This should not be viewed as a sentence. A DNA test is conducted to provide early awareness of potential cancer development.
However, there is a possibility that cancer has already begun to form. In such cases, DNA testing serves as one of the diagnostic tools at the earliest stages of the disease.
If the result is positive, it is important to:
- Consult an oncologist with your DNA test results;
- Undergo additional diagnostic procedures: X-ray imaging, cytological examinations, laparoscopy and thoracoscopy, biopsy of tumor tissue.
These investigations will help the oncologist accurately determine the stage of cancer and whether metastases are present. By combining this information with family history and DNA analysis results, appropriate treatment can be prescribed.
A comprehensive approach is typically used, combining surgery with chemotherapy or radiation therapy. The treatment plan and type of therapy are determined solely by the attending physician.
Reviews of DNA Tests and Laboratories in Moscow



































The «DTL» DNA Center conducts DNA testing throughout the entire Russian Federation. The laboratory uses equipment from Applied Biosystems, a global leader in biotechnology. Modern scientific and technological advancements enable us to perform unique DNA tests that are offered by only a few laboratories worldwide. All tests are carried out exclusively by certified specialists, including world-class experts with over 15 years of experience in DNA research.
The «DTL» DNA Center has offices in many cities across Russia, making it possible to submit samples in virtually any city, including smaller towns across the country.