DNA Test for Predisposition to Thrombophilia
Thrombophilia is a disorder of the blood clotting system that increases the risk of blood clots (thrombi) forming in the circulatory system. The condition can lead to heart attacks, strokes, tissue necrosis, pulmonary artery thromboembolism, and venous thrombosis.
Typically, thrombophilia is detected only after organ damage occurs, which is why the pathology is diagnosed in adults 10 times more often than in children.
Order a mobile service visit to your home or office.
Same-day service is available.
For a free consultation, please call:
+7 (499) 490-28-01Thrombophilia does not have any specific symptoms.
The manifestations depend on the organ where the clot (thrombus) has formed. A characteristic feature of predisposition to this disease is thrombosis occurring at a young age. In 50-60% of cases, this is the first sign of genetic thrombophilia.
Among the local symptoms, the following can be highlighted:
- Chest pain, difficulty breathing, chronic shortness of breath, discomfort during deep inhalation — signs of pathology in the lung vessels;
- Necrosis and ischemia indicate vein damage;
- Heart problems, strokes, or heart attacks before the age of 35 — point to clot formation in arteries;
- Limb pain, swelling, and impaired blood flow (occlusion) may indicate vascular thrombosis.
Special attention should be paid to thrombophilia during pregnancy. Women with this genetic disorder may experience fetal demise, developmental delays, or miscarriages in the late second or third trimester.

The studied genes

Mutations in genes responsible for the blood coagulation system significantly increase the risk of thrombophilia.
In addition, genetic predisposition combined with a deficiency of B vitamins and folic acid can lead to the development of hyperhomocysteinemia. This condition is characterized by elevated levels of homocysteine in the blood. Increased homocysteine concentration adversely affects the inner walls of arteries. As a result, blood clots can form, and atherosclerosis can develop. Hyperhomocysteinemia is particularly dangerous for pregnant women, as it can cause impaired blood circulation in the placenta.
The DNA test panel includes four genes that have a decisive impact on the blood coagulation system.
- Gene F2 — encodes the protein prothrombin (coagulation factor II). This protein is an important part of the blood clotting process. Mutations in F2 can lead to increased gene expression and, consequently, higher prothrombin levels in the blood. This significantly raises the risk of cardiovascular diseases. For example, the risk of myocardial infarction increases fourfold. Women with the pathological form of the F2 gene have an increased risk of venous and arterial thrombosis, miscarriage, or fetal developmental delays.
This gene is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner. If at least one parent passes the mutant gene to the child, its traits will manifest.
- Gene F5 — encodes the protein proaccelerin (coagulation factor V or Factor Leiden). It plays an important role in blood clotting processes. Mutations in the F5 gene lead to hypercoagulation and reduced sensitivity to the anticoagulant effect of protein C. This increases the risk of thrombosis and thromboembolic diseases. During pregnancy, it increases the risk of fetal demise and miscarriage.
The mutant gene is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner.
- Gene MTHFR — encodes the enzyme methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase. This enzyme is involved in folic acid metabolism. Mutations in the MTHFR gene sharply increase the risk of venous and arterial thrombosis.
Reduced folic acid metabolism during pregnancy can lead to severe central nervous system abnormalities in the fetus, including neural tube defects.
- Gene CRP — encodes C-reactive protein, responsible for the protective properties of blood during acute phases of inflammation. CRP concentration increases in response to injury, infection, and other inflammatory processes. Mutations in the CRP gene can lead to high CRP levels even without signs of inflammation. As a result, the risk of cardiovascular diseases can increase 4-7 times, including the risk of thrombosis.
The severity of the condition depends on the number of detected genetic markers of hereditary thrombophilia. If the test result is positive, it is necessary to consult a geneticist.
The most common form is genetic thrombophilia, caused by the presence of pathological gene variants. In women, this condition often leads to secondary infertility, while in men it can cause strokes.
A genetic predisposition test for thrombophilia is recommended if close relatives have been diagnosed with:
- thrombophilia;
- thrombosis;
- strokes;
- heart attacks and other cardiovascular diseases;
- deficiency of proteins C and S, antithrombin III.
Besides hereditary factors, there are external factors that increase the risk of thrombophilia, especially when combined with genetics:
- age over 50 years;
- pregnancy;
- use of oral contraceptives;
- cancer;
- autoimmune diseases;
- viral infections;
- major surgeries and injuries.
Men are more susceptible to this condition than women. To prevent complications associated with genetic thrombophilia, it is recommended to take a DNA test in advance.
DNA Laboratory licenses and certificates
How to take a DNA test for thrombophilia predisposition?
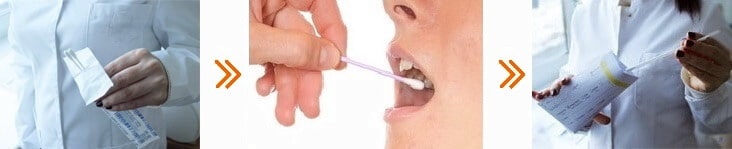
For genetic analysis, samples of buccal epithelium (oral swab) or venous blood in the amount of 5–10 ml are used.
Venous Blood
To collect blood, a vacuum tube with a purple cap is required. The tube must contain ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) of type K1, K2, or K3. The blood volume should be from 2 ml to 6 ml. Using two tubes is allowed.
The collection is performed with the patient sitting. Blood flow must go directly into the tube. After collection, shake the tube 5–6 times to mix the blood with the EDTA.
Buccal Epithelium
To collect buccal epithelium, you can visit a specialist at a biomaterial collection point or take the sample yourself at home. For this, you need:
- cotton swabs — at least 2, preferably 4;
- a clean paper envelope — 1 piece;
- a pair of sterile disposable gloves — 1 pair.
Alternatively, you can order a free collection kit by phone from our DNA center, which contains everything you need. Watch the detailed instruction with video: How to take a sample.
How long does it take?

The turnaround time for the analysis is 5 business days from the moment the samples arrive at the laboratory.
The day of sample delivery is not counted, as all samples first go through a registration process before being forwarded to the genetic specialists.
How to Receive the Report
You can receive your DNA test results in any convenient way:
- Electronically via email;
- In person at the biological sample collection point;
- By delivery through Russian Post;
- By courier delivery to your door;
- By phone (if you have a unique order number, and the phone number is authorized to receive verbal results).
The method of result delivery is selected when placing the order for the analysis.
Where to take a DNA test for a predisposition to thrombophilia
Take a DNA test for a predisposition to thrombophilia
- You can use the form «Pre-appointment» to schedule an appointment or come to our genetic center at any time convenient for you.
See step-by-step instructions see here. - Do it yourself at home:
- Order by courier our branded kit, specially designed for self-collection of DNA samples.
- Using ordinary cotton swabs (ear swabs) from a pharmacy. Our instructions.
- Order a specialist visit to your home for free.
Why the DNA Center «DTL» is the Best in Moscow
How to pay for a DNA test for a predisposition to thrombophilia
For your convenience, there are several cash and non-cash payment options for a DNA test:
- In our DNA centers, you can pay in cash or with a bank card.
- Online payment is available on our DNA center website.
- At the offices of Sberbank or any other Bank by receipt (download).
- Through a bank account (for legal entities).
When filling out an application for DNA analysis, you can choose the method of receiving the genetic test results:
- In person at the DNA center.
- To the e-mail specified in the application for analysis.
- By courier service throughout Russia.
- If you have taken a legal DNA test, we can send the forensic genetic report to the address of the court.
- If you need another delivery method, you can specify it in the application.
Each order is assigned a unique individual number. The laboratory guarantees 100% safety and confidentiality of all data received from you.
What should I do if the test is positive?
A positive test result indicates the presence of a pathological gene variant that increases the risk of developing a malignant tumor. This should not be viewed as a sentence. A DNA test is conducted to provide early awareness of potential cancer development.
However, there is a possibility that cancer has already begun to form. In such cases, DNA testing serves as one of the diagnostic tools at the earliest stages of the disease.
If the result is positive, it is important to:
- Consult an oncologist with your DNA test results;
- Undergo additional diagnostic procedures: X-ray imaging, cytological examinations, laparoscopy and thoracoscopy, biopsy of tumor tissue.
These investigations will help the oncologist accurately determine the stage of cancer and whether metastases are present. By combining this information with family history and DNA analysis results, appropriate treatment can be prescribed.
A comprehensive approach is typically used, combining surgery with chemotherapy or radiation therapy. The treatment plan and type of therapy are determined solely by the attending physician.
Reviews of DNA Tests and Laboratories in Moscow



































The «DTL» DNA Center conducts DNA testing throughout the entire Russian Federation. The laboratory uses equipment from Applied Biosystems, a global leader in biotechnology. Modern scientific and technological advancements enable us to perform unique DNA tests that are offered by only a few laboratories worldwide. All tests are carried out exclusively by certified specialists, including world-class experts with over 15 years of experience in DNA research.
The «DTL» DNA Center has offices in many cities across Russia, making it possible to submit samples in virtually any city, including smaller towns across the country.